Stages
The staging system in the table below uses the pathologic stage (also called the surgical stage). It is determined by examining tissue removed during an operation. Sometimes, if surgery is not possible right away, the cancer will be given a clinical stage instead. This is based on the results of a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests done before surgery. The system described below is the most recent AJCC system. It went into effect January 2018. It is specific for staging two types of uterine sarcomas: leiomyosarcoma and endometrial stromal sarcoma.
Uterine sarcoma staging can be complex, so ask your doctor to explain it to you in a way you understand
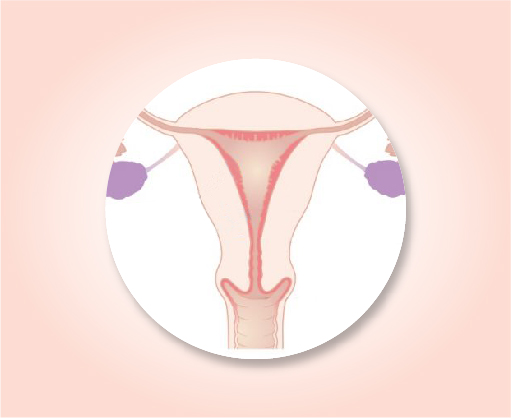
Stage 1
The cancer is growing in the uterus, but has not started growing outside the uterus. It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0).
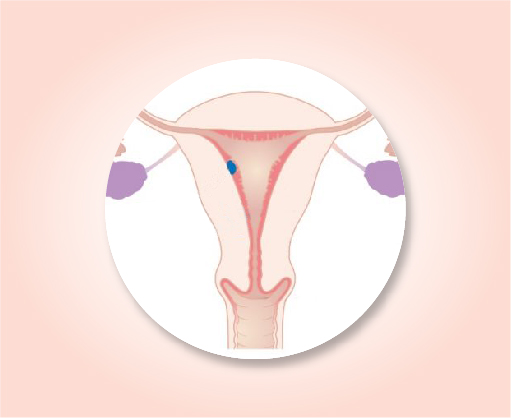
Stage 1 A
The cancer is growing in the uterus, but has not started growing outside the uterus. It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0).
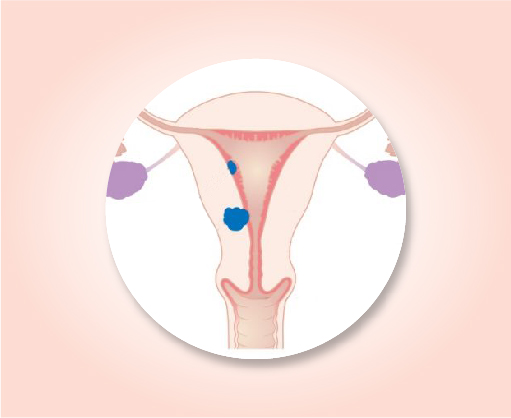
Stage I B
The cancer is only in the uterus and is larger than 5 cm across (about 2 inches). (T1b). It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0).
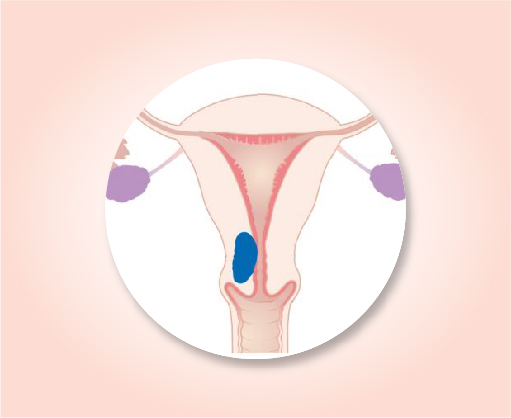
Stage II
The cancer is growing outside the uterus but is not growing outside of the pelvis (T2). It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0).
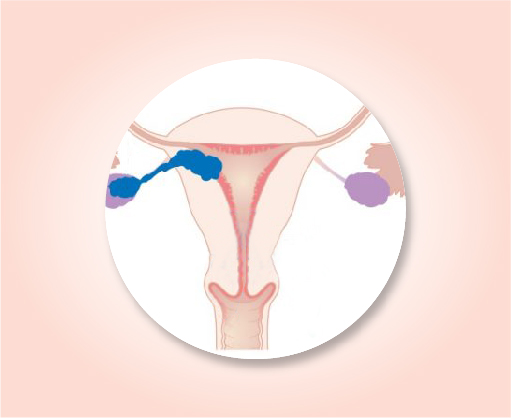
Stage III A
The cancer is growing into tissues of the abdomen in one place only (T3a). It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0).
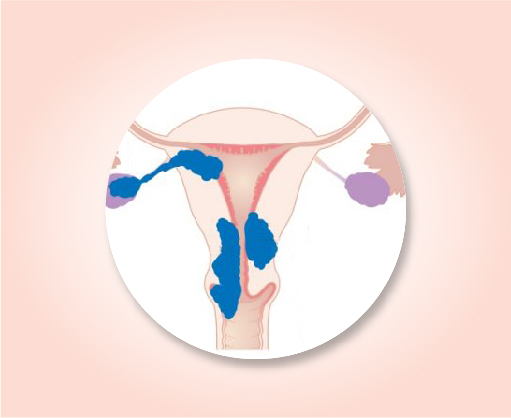
Stage III B
The cancer is growing into tissues of the abdomen in 2 or more places (T3b). It has not spread to nearby lymph nodes (N0) or to distant sites (M0).
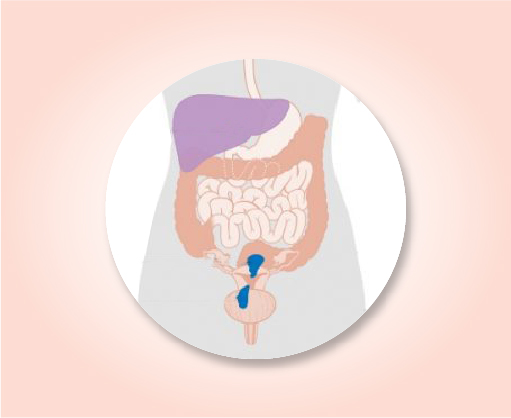
Stage IV A
The cancer has spread to the rectum or urinary bladder (T4). It might or might not have spread to nearby lymph nodes (Any N) but has not spread to distant sites (M0).
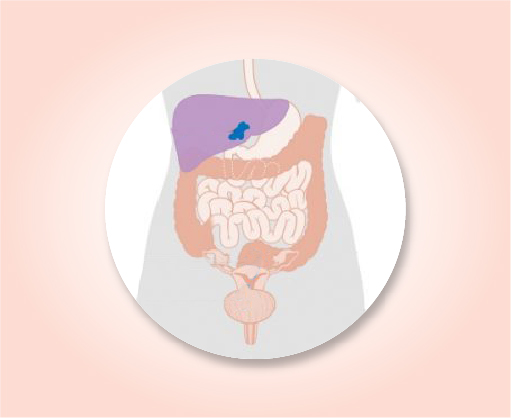
Stage IV B
The cancer has spread to distant sites such as the lungs, bones, or liver (M1). The cancer in the uterus can be any size and may or may not have grown into tissues in the pelvis and/or abdomen (including the bladder or rectum) (any T) and it might or might not have spread to nearby lymph nodes (Any N).